Join our 2nd session of MuleSoft Developing API’s session. In this session will talk about Mule 4 Message Structure and Anypoint Studio. We will also learn about MuleSoft Project Structure, Flow , Sub Flow & Private flow, Connectors and Http Listener , Set Payload connectors.
Mule 4 – Message Structure
A Mule 4 message is like an envelope that contains a letter (payload), some information on the outside (attributes), sticky notes (variables) you can attach, and a place to write down any problems that might occur (error information). All of these components work together to help you process and manage data in your Mule 4 application.
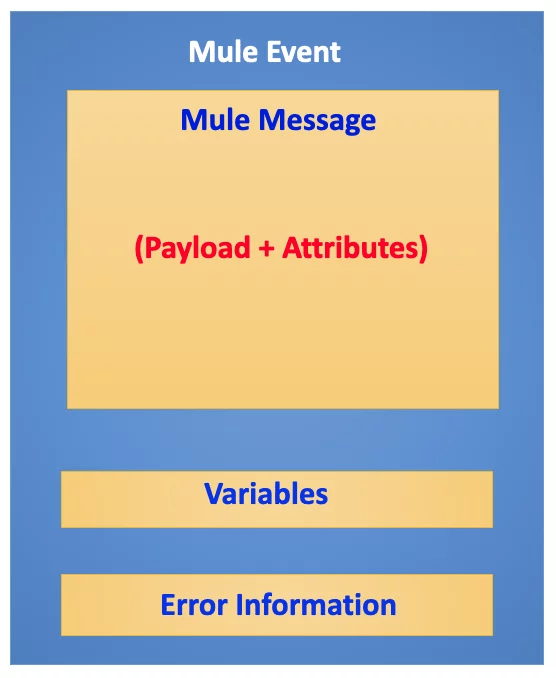
- Mule Event = Mule Message + Variables (Error Information).
- Mule Message = Payload + Attributes
Mule Event & Message Structure
- Payload : It’s the actual message content. Payload can be over ridden.
- Attributes: These provides metadata information such as queryParams, uriParams ,file size etc . These are immutable (cannot be changed)
- Variables: These are which you can store some kind of data or information and can be used across the application as long as you connect the flows with flow-ref .
- Error Information : In case any error occurs in the application, an error object is produced which contains all the information related to the error
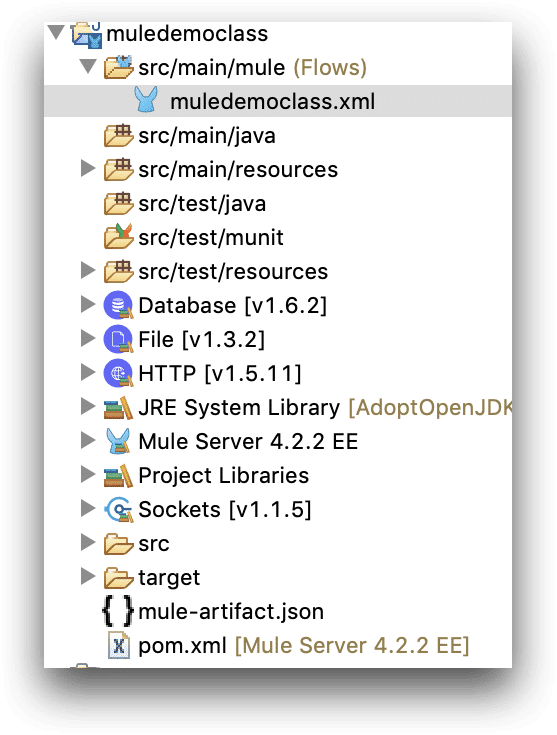
Mule Project Structure
- Every Project in Mule 4 is Mavenized Project (pom.xml)
- All Mule xml’s are placed under src/main/mule
- Other files can be placed under : src/main/resources or src/test/resources
- mule-artifact.json
- Each Mule app xml has – Message flow (Graphical view) , Global elements(contains all config details) ,configuration xml (xml version of graphical view)
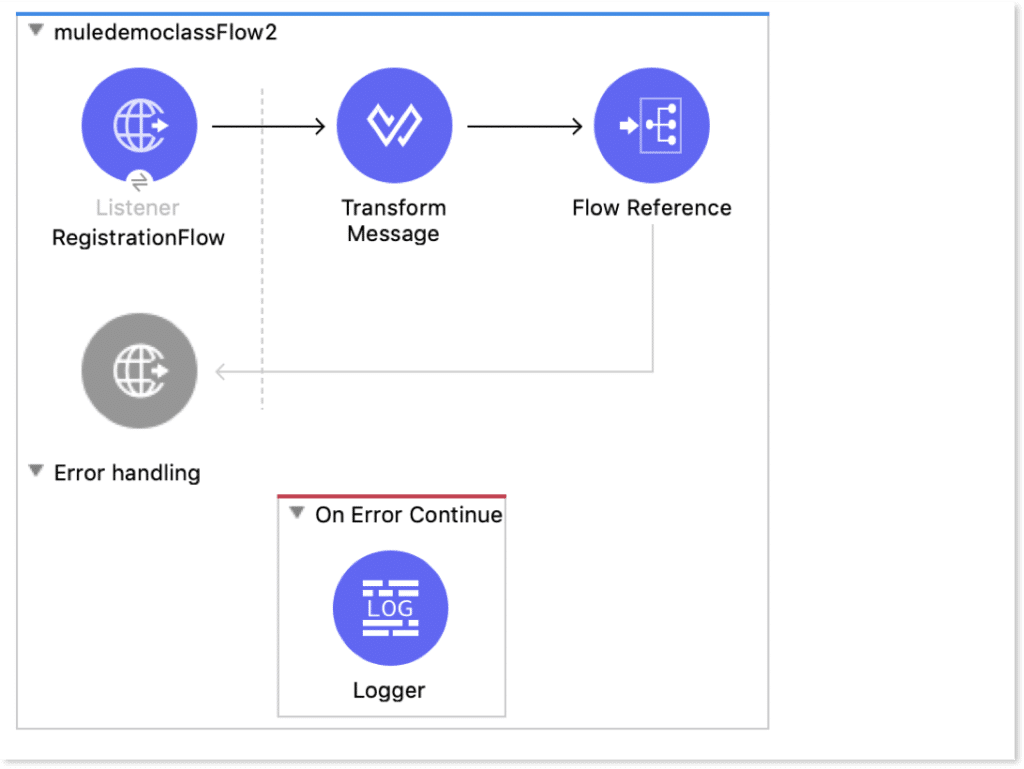
Flow , Sub-flow & Private Flow
- An App can consists of a single flow !
- Or it can break up processing into discrete(private) flows and sub flows that you add to the app and connect together.
- Private and sub-flows can be triggered by Flow-reference or by DataWeave lookup!
Flow
A flow has “Source” , “Process” and “Error Handling” Part. You should definitely keep something in Source.
Private-Flow
A private flow has “Source” , “Process” and “Error Handling” Part. It’s called a private flow when we don’t keep anything in Source Part.
Sub-Flow
A sub flow do not have “Source” and “Error Handling” Part. It has only Process Part. Error Handling for sub-flows are handled by the calling flow/private flow.
HTTP Listener
- Listens to the request which client/user sends.
- Mandatory Config Details required: host , port , path
- Default : Accepts all kind of Methods if nothing is specified
Set Payload
- The Set Payload component lets you update the payload of the message.
- The payload can be a literal string or a DataWeave expression
- Mandatory Config Details required: value eg : #[“Hello World” ] or #[payload] or #[attributes.queryParams.name]
- Default : #[payload]
Summary
Checkout our complete MuleSoft Training to learn all about MuleSoft. We have 15+ session for you with Final Project.






Your Clean and understandable way of explained the mule event. Thanks a lot