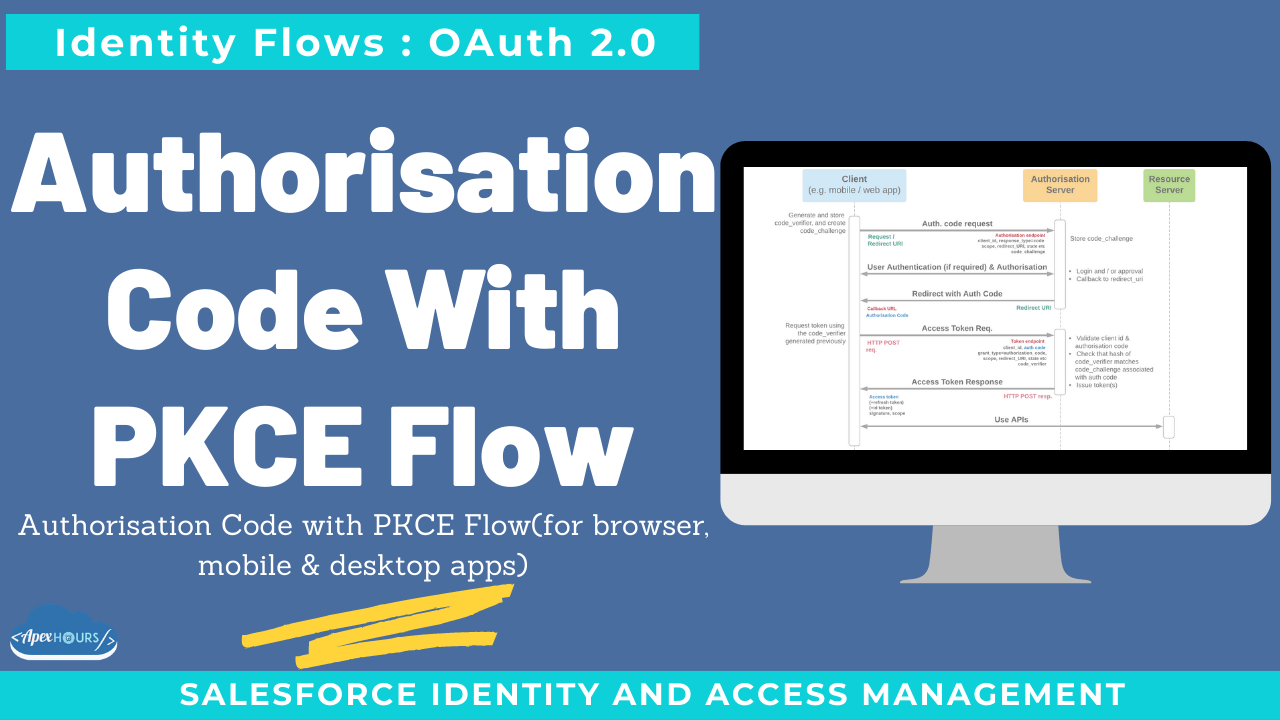
This post will discuss Authorisation Code with PKCE Flow(for browser, mobile & desktop apps). A variation of auth. Code flow for clients that can’t protect a global secret. Better security than implicit grant / user-agent for similar use cases.
Additional requirements
- Browser – for a user to authenticate and consent
- The client can generate and securely store a code_verifier
- Up-to-date security measures
What else to know about
Proof key for code exchange supported by SHA256:
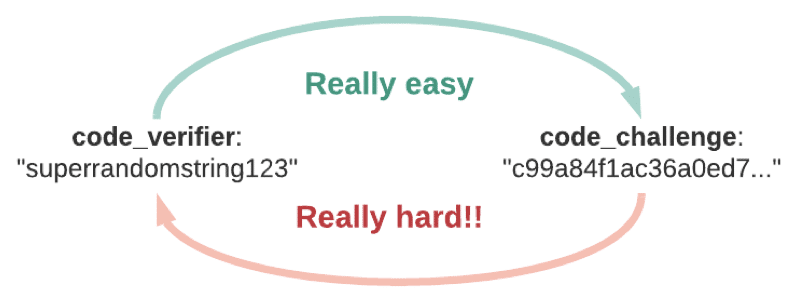
- Access token leakage risk is reduced with HTTP POST
- POST request/response protects against access token injection
- More secure channels can be used for token requests if available.
- Security recommendations
| Vulnerability | Protection |
| PKCE downgrade | Auth server must enforce all requests for a given configuration to require code_challenge |
| CSRF | Use and verify state and nonce for request/response binding |
| Redirect to an attacker’s page | Client must not allow open redirects Auth server must not allow open redirects or pattern matching of redirect_uri |
Considerations for choosing authorization code + PKCE
- Auth code requests can be over a relatively open channel
- Ideal for mobile, SPA, desktop apps, etc, where no secure client-server is involved
- Requires auth—server to support PKCE.
Learn more.
Summary
I hope this video will help you to understand the Authorisation Code with PKCE Flow in Salesforce. Learn more about Oauth Authorization flows in Salesforce.